1.7. Materiality analysis
Considering the internal sustainability management structure, the responsibility for the sustainability reporting and transparency in qualitative and quantitative data is coordinated each year by the Sustainability Director. After the integration of data and development of the sustainability report, the CEO (the highest governance body) approves the final form of the report, after verification and review of its alignment with the sustainability strategy.
Since 2021 when we developed the Sustainability Strategy for Autonom we have focused on identifying and analysing material topics relevant to our work. We carry out this analysis year after year by carefully analysing our activities and the added value in our value chain considering a careful analysis on risks and opportunities. The analysis was conducted considering the value chain and the extent of our interactions with different stakeholders as well as the relevant material issues or topics at each stage in the chain. We reflected on the impact our business has on the environment and society but also what could be the influences coming from outside that could affect our business financially from a business relevance perspective. It was very important to identify those topics on which we focus our processes in the sustainability management system but also the operational strategy for effective control and monitoring of operational indicators through specific processes to prevent negative impacts.
For the first time we are doing an exercise in double materiality analysis. For this process the consultation part of the internal and external stakeholder consultation is a defining part in the development of the materiality matrix both from the internal perspective of management’s position on key issues and from the perspective and view of other internal and external stakeholders. Also, in order to apply the perspective of the impact of the external environment on the business we conducted interviews with internal management but also with external managers of the organisation (from the customer group). 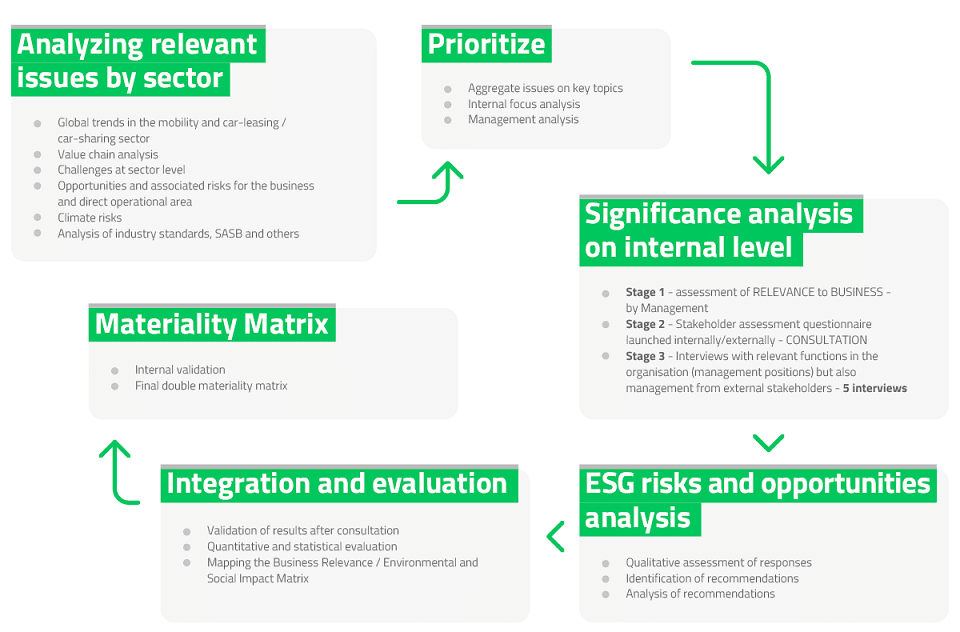
With the annual review of the list of material topics, for the 2022 activities, synergistic issues were identified from an operational perspective with potential impact that we wanted to aggregate so we defined the new topic “Resource Management” where we agreed to address the energy and fuel issues used for the company’s own fleet. We also renamed last year’s topic “Waste & Hazardous Materials Management” to “Waste & Hazardous Materials”. We have introduced for this year’s analysis, evaluation and presentation a new but relevant material topic for our business, namely “Economic Performance”.
The material themes relevant to the company are:
Sustainable business and governance | |
Corporate Governance and Compliance | The conduct of our business is based on the principles of integrity, transparency and respect for society and the environment, with a systematic approach to risk management and compliance. |
Economic Performance | Achieving our strategic goals and objectives leads to business growth and development and contributes to the local economy (by paying salaries and taxes etc.). We support green economic development by providing sustainable mobility solutions in local communities and business segments. |
Supply Chain Management | Through partnerships, we promote Autonom values in our social and business interactions, including in the value chain. We develop customised services together. |
Business Ethics and Transparency | We identify this aspect of materiality as fundamental to our company. We are committed to respecting and promoting fair and honest business practices. We have zero tolerance for bribery and corruption, wherever and in whatever form it may occur. |
Data Security | Data security and cyber protection is important to us. We apply the right solutions so that we can continue to ensure the security of all the customer data we manage. |
Customer Satisfaction, Sales and Market Practice | We see fair practices as the only tools that can help us show respect for the development of the market and its demands. We also respect our competitors and focus primarily on the needs of the market. |
Environment | |
GHG Emissions and Climate Impact | Global warming due to GHG (greenhouse gas) emissions from human activities is a challenge for mankind. We are committed to contributing to mitigation through a transition to sustainable mobility that is in line with our customers' requirements. |
Resource management | Proper management of energy, fuel and other resources involved in the daily routine of our operations can lead to environmental, social and economic benefits. |
Waste and hazardous materials | The results of our work can generate some significant negative environmental and economic impacts. We strive to manage waste properly by maintaining appropriate recycling actions. |
People and community | |
Community Involvement | Our employees are an active part of their communities and are constantly involved in education, social and sports projects. Our responsibility to be involved in the community, around education, has materialised in particular through the projects run by the Autonom Foundation. |
Employee Health and Safety | The needs of our employees, who play a vital role in the success of our business, are met with the equipment, devices and instructions needed to ensure a safe workplace. |
Employee Well-being and Developmen | Attracting and retaining talented people is achieved by providing a friendly and safe working environment where a positive attitude is key to the well-being of our employees. We emphasise personal development as a daily practice and focus on this in our half-yearly appraisals. |
Quality of Education | Projects to promote learning and reading in our communities and to our partners help raise awareness of more sustainable behaviour and climate action. |
Diversity, Equality & Human Rights | We encourage diversity and do not tolerate any hostile behaviour in this regard. We treat this subject with the utmost care and ensure that human rights are always respected in our company and in other external contexts. We value gender equality and have a strong position on women in leadership positions. |
Working Conditions | We want to provide the best solutions about ensuring proper working conditions for our employees. We customize and equip all our work areas with the materials necessary for our field of business. |
The materiality analysis methodology followed the concept of double materiality, the quantitative assessment of Autonom material issues considering:
- relevance to the
business – outside-in perspective - social and environmental impact of the organisation in the
community – inside-out perspective
Each material topic (of the 15 material topics) has an economic impact on the company (business relevance dimension) and an impact on the environment and society (community impact dimension), and explanations of the different types of impacts on economic, social and environmental factors are provided in this report for each material topic in separate chapters.
The concept of double materiality was integrated into the stakeholder consultation process, for which we used three stakeholder engagement methods:
Stakeholder consultation method | Outcome/purpose |
|---|---|
Online questionnaire launched internally/externally | Quantify the impact of the organisation on the community for each material aspect identified (inside-out perspective) 391 replies |
One-to-one interviews with internal/external management functions | Quantify the relevance to the business of each material aspect (outside-in perspective) 5 interviews |
To conclude the report and focus our efforts to be transparent and responsive to our stakeholders’ recommendations in
A total of 391 responses were aggregated and evaluated. The split of responses is balanced INTERN/EXTERNAL. It can be seen that a large proportion of respondents are internal stakeholders (employees) but this is explained by the fact that their number is much higher. The large number of responses from employees is good for us because they have contributed to our important journey in sustainability performance reporting and definition of important new actions. We are also grateful that people from all key Autonom stakeholder groups responded to our survey requests.
The final quantification and evaluation of the results and the definition of the double materiality matrix considered certain limitations according to the stakeholder mapping results.
Recommendations from our stakeholders throughout the survey are highlighted in the chapter “Our engagement and relationship with stakeholders”.
Group/stakeholder category | Stakeholder groups | Response split, % |
|---|---|---|
INTERNAL | Management | 6.65% |
INTERNAL | Agency employee/support function (Self-employed) | 43.99% |
EXTERNAL | Public Authority/House | 0.26% |
EXTERNAL | Customer | 34.53% |
EXTERNAL | Service provider/direct materials/utilities/other | 6.65% |
EXTERNAL | Investor/Analyst/Bank Representative/Rating Company | 1.02% |
EXTERNAL | Media (press/social media) | 0.51% |
EXTERNAL | International/Local NGO/Professional Association | 1.79% |
EXTERNAL | Neighbours/Owner space rented by the company | 0.51% |
EXTERNAL | University/School/Kindergarten | 2.81% |
EXTERNAL | Another category | 1.28% |

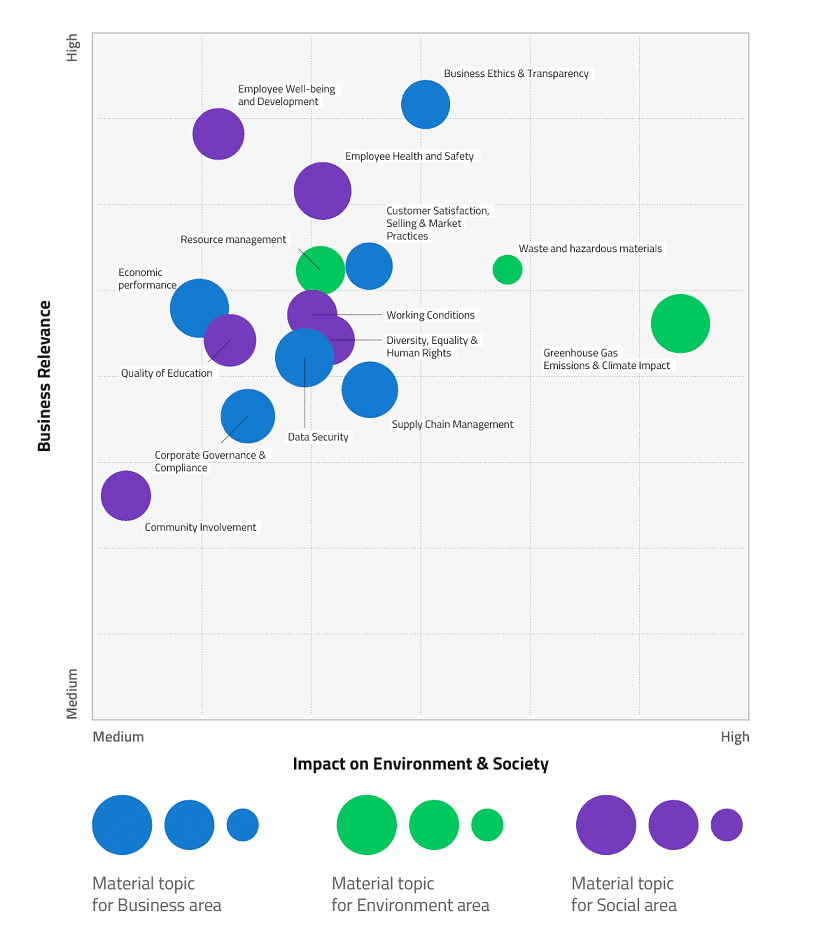
Materiality Matrix
The results of the consultation process through questionnaires and interviews helped us to define the materiality matrix but also to highlight a list of risks and opportunities.
Delineation of the material topics on which reporting and disclosure focused was done from two perspectives:
- the potential size of the impact in the community (environment and social), their control and management
- relevance to the business and highlighting the potential impact on financial capital of those material issues that bring more risks than opportunities if not managed in a balanced and compliant way at business level
The limits of material issues
Dimension/Material issue/Type of stakeholder | Scope / Limitations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
INTERN | Limitations | EXTERN | Limitations | |
Business | ||||
Corporate Governance & Compliance | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Economic performance | AUT | AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Supply Chain Management | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Business Ethics & Transparency | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Data Security | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Customer Satisfaction, Selling & Market Practices | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Environment | ||||
Resource management | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Waste and hazardous materials | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Greenhouse Gas Emissions & Climate Impact | AUT | F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Social | ||||
Community Involvement | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Employee Health and Safety | AUT | C, F, IARB, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Employee Well-being and Development | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Quality of Education | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Diversity, Equality & Human Rights | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Working Conditions | AUT | C, F, IARB, AUP, M, ONG, PS, U, V, ALT | ||
Note:
Interpretation of results
Relevance to business
The quantification of the business relevance of each material issue was determined using data collected in one-on-one interviews, which provided information on opportunities and risks for each material issue.
Impact of the organisation in the community
Quantification of the organisation’s impact on the community considered the positive and negative impact generated by each material aspect on environmental and social factors, using as input the ratings given by stakeholders in the online questionnaire.
The matrix shows the importance of material topics for stakeholders from a stakeholder decision-making perspective and highlights those material topics that may have an impact on the environment or society.
Throughout the interviews we identified risks and opportunities which we detail below. These are well known internally, and processes are in place to address them. Opportunities will always find a very high share in being addressed quickly and risks are mitigated by various actions to prevent negative effects or undesirable financial impact.
Pillar | Identified risks | Opportunities identified |
|---|---|---|
Business | Marketing or communication events that go against organisational culture and principles | Potential for business growth through diversification of the service portfolios offered but also by the increasing maturity of the markets in which we operate |
Business development along with the need for digitisation can bring operational synergy | ||
Increased cyber-attacks are leading to the migration of organisational systems to the cloud which does not mitigate the risks across the board. | Testing new secure systems with very low risk of breaches. Continuous testing already exists within the organisation | |
Reduced availability at dealers for LEV machines. Increased delivery times of cars which can lead to customer dissatisfaction | Satisfied customers will recommend Autonom services further | |
High-performance LEVs with a long range are very expensive | Customer awareness for substitution | |
State does not support substitution of the organisation's fleet for the LEV fleet | We address the incentive and allocation of the spherical profit | |
Environment | Limiting resources where we have no control. Uncontrolled price increases or rationing | Supporting customers in the transition to low carbon mobility (electric, hybrid) |
Poor national infrastructure for charging electric cars | Generating business and partnerships in the field of waste recycling and reuse | |
Business reluctance to make the transition to low-emission cars due to lack of charging infrastructure | Generate collaborations and customers by offering fuel-only cars for inter-city travel. The use of LEVs in the urban environment. | |
Insufficient data on long-term maintenance costs for LEVs | Procurement of long-range LEVs. customer awareness and education | |
We work with polluting assets | We come up with sustainable mobility solutions and are aware of the transition for our customers | |
Social | Loss of interest among young people in education, specific skills in general may lead to a shortage of staff in the future | Internal and external collaborations at the top of the needs pyramid |
Employee overload from customers can lead to stress | Entrepreneurial education of young, future employees Autonom. Pleasant working conditions, a permanent care for employees | |
The area of remuneration has a significant impact in attracting people with skills. | We support and make room for innovation. A continuous opportunity. Maintaining organisational culture. "Learning Organization", the confidence we give employees the power of transformation. |
